In the past few years, the Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI) sector has experienced a significant increase in digital consumption demand. This surge can be attributed to customer expectations for improved experiences and the adoption of flexible work arrangements for business operations.
To add, financial institutions are overburdened with complex legacy software systems. These systems can hinder the Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI) sector’s ability to be agile and can cause delays in introducing new products and services to the market. Plus, there’s mounting pressure on BFSI companies to remain competitive amid an already volatile market.
As a result, there is now a higher need for skilled developers who can handle the legacy technology setups. However, the rapid rate of digital transformation has led companies to allocate their scarce development resources toward customizing workflows and routine tasks. This focus on day-to-day operations has taken precedence over pursuing innovative initiatives and essential product development.
Here are some of the pressing questions for Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI) business and product leaders:
- Which emerging technologies are essential for BFSI companies to embrace in order to maintain a competitive edge?
- How can BFSI organizations align themselves with the rapid pace of technological advancements?
- How can BFSI firms update their offerings to meet the ever-changing customer demands?
- Low code/no code appears to be the answer to most if not all the questions. Here’s why?
What are Low code/no code (LCNC) platforms?
Low-code and no-code platforms simplify the process of creating computer programs and apps.
Low-Code Platforms: They utilize visual interfaces to combine pre-made components for faster app creation, requiring some coding knowledge.
No-Code Platforms: They offer even simpler creation with no coding; users customize templates via visual interfaces. Ideal for quick app building without coding skills.
Gartner projects the global low-code market to reach $26.9 billion in 2023 (19.6% growth from 2022). By 2024, low code/no code will account for over 65% of all application development
Low code/no code has established itself as one of the most promising technological trends and no industry, especially BFSI should lag behind in its adoption and innovation.
Low code/no code in the Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI) Industry
In the BFSI sector’s ever-changing landscape, low code/no code can be used to simplify processes such as compliance, customer onboarding, loan approvals etc. The technology also allows BFSI firms to easily adapt to regulatory shifts and changing customer needs. Furthermore, these solutions facilitate the easy creation of personalized digital experiences, such as customized financial dashboards, without requiring extensive coding skills.
Let us look at some of the key technical features of low code/no code platforms
1.AI powered tools: Today, no business can innovate without effectively using AI technology. Low-code/no code platforms empower BFSI tools to create AI driven apps such as chatbots, fraud detection systems etc. and deploy them in quick time.
2.Visual modelling tools: Low-code systems come with visual modelling tools that utilize ready-made modules to represent information in a manner comprehensible to both non-technical professionals in the BFSI industry and advanced developers.
3.Drag and drop interfaces and pre-built templates: Drag-and-drop features are a key feature of low-code/no code platform. Another big part is that most major functionalities are already pre-built into modules that can just be dragged and dropped wherever required.
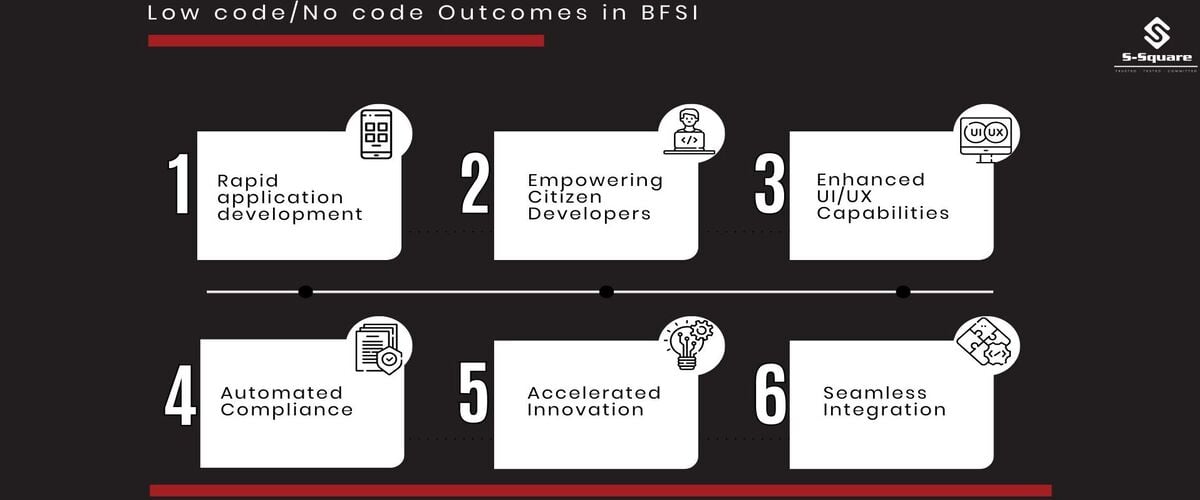
Modern challenges need modern solutions: Comparing Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI) challenges with low code/no code outcomes.
Let us now compare some of the BFSI challenges and the resolutions offered by low code/no code.
Challenges in BFSI Sector |
Low-Code/No-Code outcomes |
| Complex Legacy Systems: Hindered agility and innovation due to legacy infrastructure. | Rapid Application Development: Low-code/no-code enables faster app creation, modernizing processes without extensive coding. |
| Talent Shortage: Scarcity of skilled developers affects software development speed. | Empowering Citizen Developers: Low-code platforms allow non-developers to create apps, reducing dependency on scarce talent. |
| Customer Expectations: Demand for personalized experiences and quick services. | Enhanced UI/UX Capabilities: Low-code/no-code facilitates designing user-friendly, customized apps for improved customer satisfaction. |
| Regulatory Compliance: Struggle to adhere to evolving regulations and standards. | Automated Compliance: Low-code/no-code enables automation of compliance tasks, ensuring accuracy and timely adherence. |
| Innovation Pressure: Need to innovate amidst intense competition from fintech and tech companies. | Accelerated Innovation: Low-code/no-code expedites software development, fostering innovation and competitiveness. |
| Integration Challenges: Integrating disparate systems and processes smoothly. | Seamless Integration: Low-code/no-code platforms offer easy integration with various systems, improving data flow and efficiency. |
Case Studies: Low code/ No code in action for Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI) Industry
Few interesting case studies where BFSI firms have realized low code/no code benefits are:
- Revolut’s identity verification program: Revolut, a fintech startup, adopted a no-code SMS API with two-factor authentication to securely verify user identities worldwide. This ensured authentic users and enabled effective customer support.
- Standard Bank’s Digitization Hub: Standard Bank, established a center of excellence empowering business units in their digitization journeys. A remarkable achievement involved a low-code ATM inspection solution, with a prototype app developed in just 24 hours. Over 300 inspectors now use it, generating 5,000+ reports monthly.
- Piraeus Bank’s innovation with low code: Facing IT challenges post-acquisitions, Piraeus Bank embraced low code to launch multiple applications. This benefited 6,500+ users, fostering operational efficiency and core activity enhancement.
S-Square for Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI) low code/no code (LCNC) services
S-Square leads the way in using low code/no code to create advanced applications. With many clients served, we’ve effectively used the technology to create tailored offerings that address your immediate and long-term app development needs.
Our key differentiators are:
- Developing effective processes, procedures, and centers of competence for successful tool implementation within the client environment.
- Continued support, including development and maintenance.
- Legacy application modernization, application integration, and digital transformation.
Our key low code/no code (LCNC) services include:
- Visual Development: By using our low code/no code Platform, you can simultaneously build the back-end and front end interface of your app and see your app develop in real-time. This visual approach makes it simple to continuously improve and enhance any app.
- Integration: By using open standards and technologies like JSON, SOAP, XML, OData, and REST, data can be easily exchanged through web requests, resulting in seamless connection of your application with other systems and apps.
- Empowering UI/UX Features: By utilizing our UI/UX capabilities, you can easily design user-friendly and powerful apps. There’s a variety of customizable design templates to pick from, giving you the best tools to create.
Explore our low code/no code offerings in detail here and our offerings in the Banking and financial services sector here
No code/Low code (LCNC) best practices.
Below are some of the best practices from an implementation and collaboration perspective.
-
Effective implementation:
-
- Enterprise-level deployment: Consider no-code as an enterprise platform, not just an individual tool.
- Formal training and management: Provide proper training and implement management controls.
- Metrics and governance: Monitor usage with metrics and integrate within policies for better governance.
- Mitigating technical risks: Ensure deployment doesn’t introduce technical risks to the environment.
-
-
Collaboration and Clarity:
-
- Senior leadership support: Leadership should emphasize that no-code platforms free up capacity for complex tasks.
- Business-technology partnership: Success relies on a strong collaboration between business and technology teams.
-