Rank ():
RANK function is used to rank the repeating values in a manner such that similar values are ranked the same. In other words, rank function returns the rank of each row within the partition of a result set. The rank of a row is one plus the number of ranks that come before the row in question. The RANK () function is also useful to find the top-N and bottom-N reports.
Syntax:
SELECT RANK () OVER (PARTITION_BY_Clause ORDER_BY_Clause) FROM [Source]
Partition_by_clause:
This is used to splits the rows generated into different sets. If partition_by_clause is not specified, then all rows shall be treated as a single group.
Order_By_Clause:
This is used to sort the Partitioned data into specified order.
Example for Rank Function
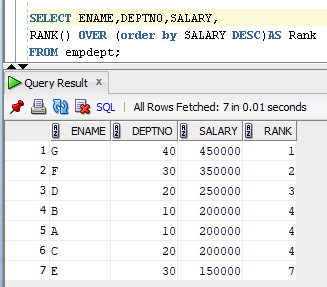
In the above example we can see the value of salary 20000 is repeated for 3 times and we have same rank number 4 is repeated for 3 times and next rank value is 7.
Example for RANK function with partition:
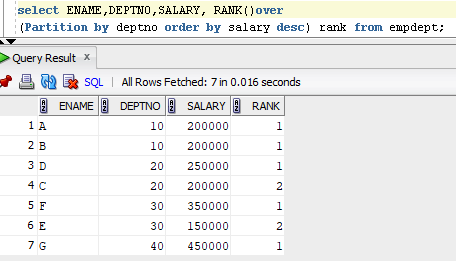
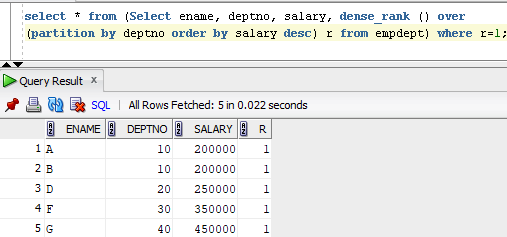
In the above Output we can see the rank is partitioned (Grouped) by DEPTNO.
DENSE_RANK ():
The DENSE_RANK () will assign the rank number to each record present in a partition without skipping the rank numbers. dense_rank function returns the rank of each row in continuous series within the partition of a result set. The rank of a row is one plus the number of distinct ranks that come before the row in question.
Syntax:
SELECT DENSE_RANK () OVER (PARTITION_BY_Clause ORDER_BY_Clause) FROM [Source]
Partition_by_clause:
This is used to splits the rows generated into different sets. If partition_by_clause is not specified, then all rows shall be treated as a single group.
Order_By_Clause:
This is used to sort the Partitioned data into specified order.
Example for DENSE_RANK Function:
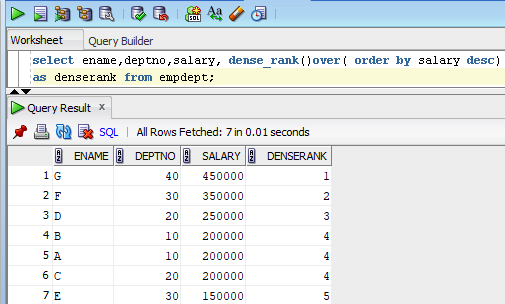
In the above example we can see the value of salary 20000 is repeated for 3 times and we have same rank number 4 is repeated for 3 times and next rank value is 5.
Example for DENSE_RANK function with partition:
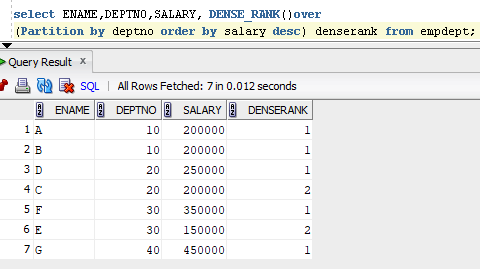
For DENSE_RANK function the rank is partitioned(Grouped) by DEPTNO.
Query to find the Nth Highest Salary in the table:
In order to find nth highest salary in the table we use RANK () or DENSE_RANK () based on requirement.
Syntax:
Select column1, column2… RANK ()/DENSE_RANK () over (Partition by column name order by column name) R form Table name;
Below is the sample table data with ranks:
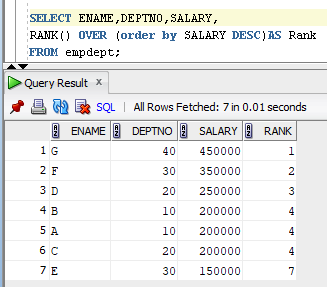
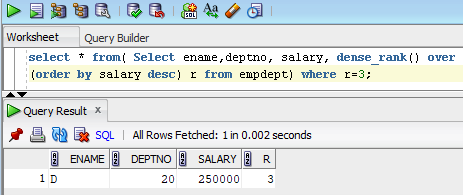
To find the 3rd highest salary below is the Query:
select * from (Select ename, deptno, salary, dense_rank () over
(order by salary desc) r from empdept) where r=3;
To find the 1st highest salary Department number wise: